I. Introduction
A. What is Myocardial infarction (Heart Attack)?
Myocardial Infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is a severe medical condition wherein the flow of blood to the heart is blocked. This often results from a buildup of fatty substances, cholesterol, and other elements, leading to severe health complications or even death if not treated promptly.
B. Importance of Understanding Symptoms, Causes, Precautions, and Risk Factors
Knowledge is power. Knowing the ins and outs of myocardial infarction can mean the difference between life and death. This blog aims to shed light on its symptoms, causes, precautions, and risk factors, equipping you with the information you need to take control of your health.
C. Scope of the Paper
This blog will delve into the signs to watch for, the underlying causes, lifestyle modifications for prevention, and what puts you at risk for this life-altering event.
II. Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction
A. Chest Pain
1. Quality of Pain
The pain can be excruciating and is usually described as a sensation of tightness, squeezing, or pressure on the chest.
2. Duration
It can last for more than a few minutes or go away and return.
B. Shortness of Breath
You may experience difficulty breathing, often irrespective of physical exertion levels.
C. Additional Symptoms
1. Sweating
Cold sweats are a common symptom, unrelated to temperature or physical activity.
2. Nausea
Feelings of indigestion or an upset stomach can occur.
3. Fatigue
A sudden and unexplained feeling of extreme tiredness can accompany a heart attack.
D. Silent Myocardial Infarction
1. Asymptomatic Cases
Some people experience no symptoms at all during a myocardial infarction, which is known as a ‘silent’ heart attack.
2. At-risk Populations
Older adults and people with diabetes are more likely to experience a silent myocardial infarction.
E. How Symptoms Differ Between Genders
Women may experience atypical symptoms like jaw pain, back pain, and abdominal discomfort.

III. What is the immediate treatment for Myocardial infarction?
The immediate treatment of MI include, taking aspirin, which prevents blood from clotting, and nitro-glycerin to treat chest pain and oxygen.
The heart attack can be prevented by taking an earlier action to lower those risks by controlling diet, fat, cholesterol, salt, smoking, nicotine, alcohol, drugs, monitoring of blood pressure every week, doing exercise every day, and loosing body weight.
The treatment of MI includes, aspirin tablets, and to dissolve arterial blockage injection of thrombolytic or clot dissolving drugs such as tissue plasminogen activator, streptokinase or urokinase in blood within three hours of the onset of a heart attack.
IV. Causes of Myocardial Infarction
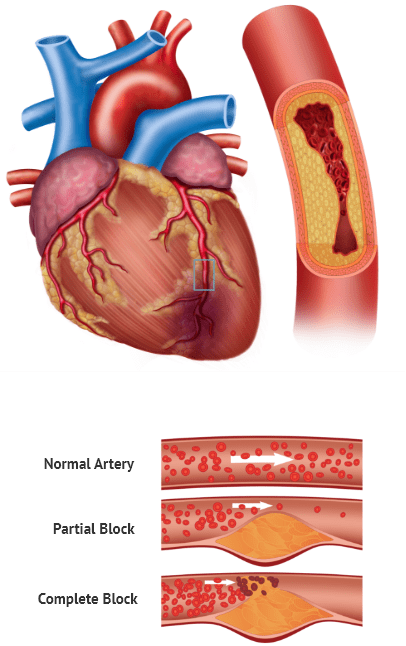
A. Coronary Artery Disease
1. Plaque Buildup
Fatty deposits can accumulate on the walls of your coronary arteries, restricting blood flow.
2. Artery Narrowing
Narrowing further restricts the blood flow and can lead to angina or a heart attack.
B. Blood Clots
A clot may travel from elsewhere in the body, blocking the arteries that lead to the heart.
C. Spasm of a Coronary Artery
Sudden constriction of the heart muscle can temporarily decrease blood supply to the heart.
D. Torn Blood Vessel
Though rare, this can also cause a heart attack.
E. Other Causes
1. Drug Abuse
Stimulant drugs like cocaine can trigger a heart attack.
2. Trauma
Physical damage to the heart or its arteries can result from an accident, further endangering your heart health.
V. Precautions
A. Lifestyle Changes
1. Diet
Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can support heart health.
2. Exercise
Regular physical activity can fortify your cardiovascular system.
B. Medications
1. Aspirin
Under medical supervision, aspirin can sometimes help prevent heart attacks.
2. Statins
These are cholesterol-lowering drugs that can reduce the risk of heart attack.
C. Medical Procedures
1. Angioplasty
This procedure can open up blocked arteries.
2. Bypass Surgery
Severely blocked arteries may require a bypass surgery for effective treatment.
D. Monitoring
1. Regular Check-ups
Annual medical evaluations can help you and your healthcare provider keep tabs on your heart health.
2. Stress Tests
These can monitor how your heart performs under stress and can be vital in predicting your heart-attack risk.
VI. Risk Factors
A. Age
People over 65 are at a higher risk.
B. Family History
Genetics can play a role in your likelihood of suffering a heart attack.
C. Lifestyle Choices
1. Smoking
Tobacco use significantly increases your risk.
2. Poor Diet
A diet high in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium can elevate your risk.
D. Existing Medical Conditions
1. Diabetes
High sugar levels can damage your arteries.
2. Hypertension
High blood pressure can cause your arteries to weaken or harden, leading to heart disease.
E. Psychological Factors
1. Stress
Chronic stress may contribute to heart problems.
2. Mental Health
Conditions like depression can affect your heart health.
VII. Who is at Risk for a Heart Attack?
- People with inherited high blood pressure (hypertension).
- People with inherited low levels of HDL cholesterol, high levels of LDL cholesterol, or high levels of triglycerides.
- People with a family history of heart disease. This is especially true if the heart disease started before age 55.
- Older men and women.
- People with type 1 diabetes.
- Women who have gone through menopause.
- Cigarette smokers.
- People who are under a lot of stress
- People who drink too much alcohol.
- People who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
- People overweight by 30% or more.
- People who eat a diet high in saturated fat.
Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points
Myocardial infarction is a severe medical condition that requires immediate attention. Awareness of its symptoms, causes, precautions, and risk factors can make all the difference.
B. Importance of Awareness and Early Intervention
Your life literally depends on how quickly you act on these symptoms. Early intervention can be a life-saver.
C. Recommendations for Further Reading and Consultation with Medical Professionals
Please consult your healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment tailored to your individual needs.
📍 English Language Educator | Blogger & Content Strategist | 7+ Years in Educational Blogging
Nosheen Bashir is a dedicated English teacher and experienced blogger with over seven years of expertise in content creation and educational writing. Passionate about language, literature, and effective communication, she combines her teaching experience with blogging skills to create insightful, research-backed content that helps learners and educators alike.
🔹 Expertise & Achievements:
✔ English Language Education: A skilled educator with years of experience in teaching English grammar, literature, and communication skills to students of varying levels.
✔ Educational Blogging: Running a successful blog for 7+ years, delivering well-structured, engaging content on language learning, writing techniques, and academic success.
✔ SEO & Content Strategy: Specializes in creating high-ranking, authoritative articles that follow Google’s EEAT principles, ensuring content that is both informative and search-friendly.
✔ Student-Centric Approach: Committed to making English easier, engaging, and accessible, helping readers and students improve their language proficiency.
🚀 With a passion for teaching and writing, Nosheen Bashir is dedicated to crafting educational content that empowers students, teachers, and language enthusiasts worldwide.