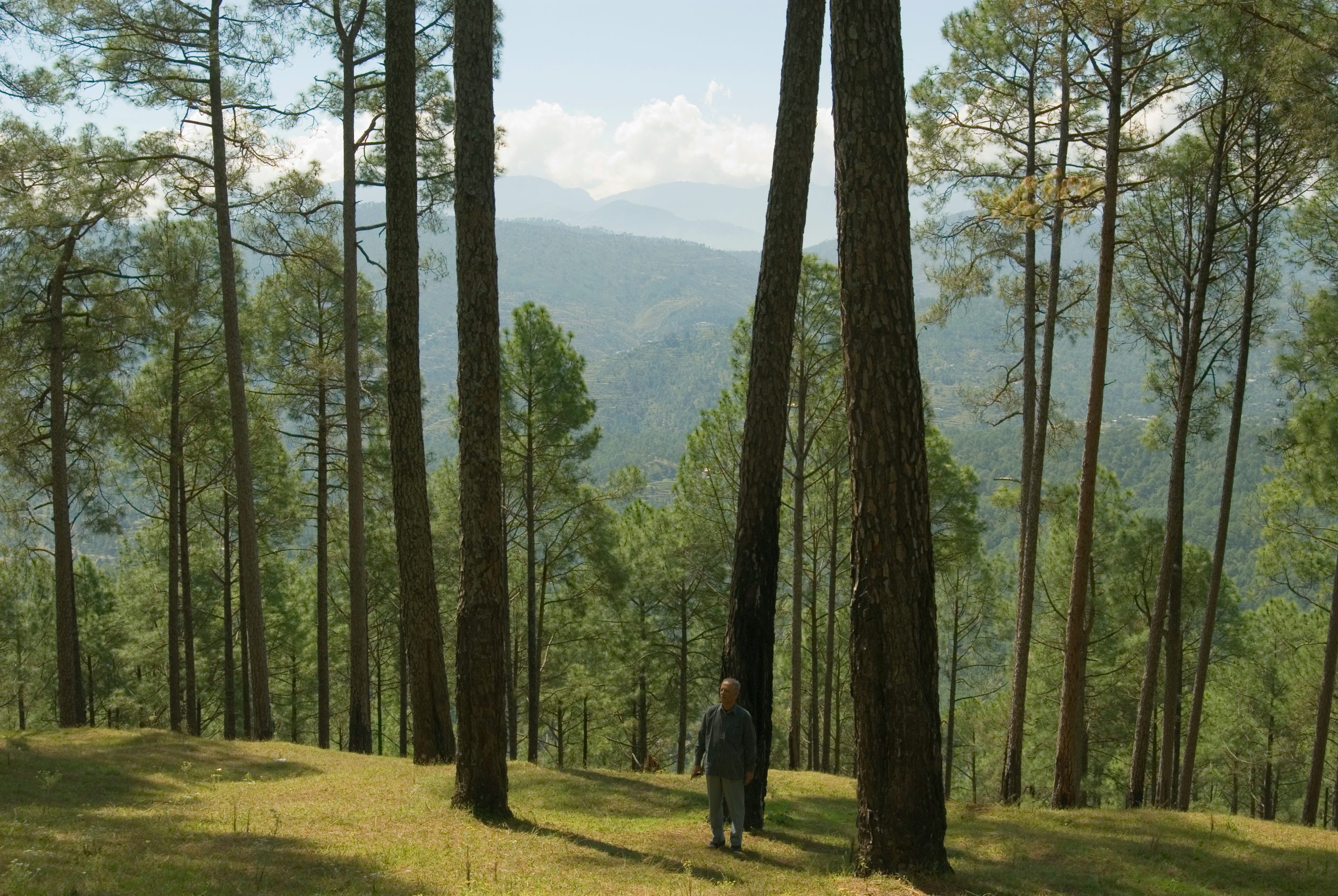
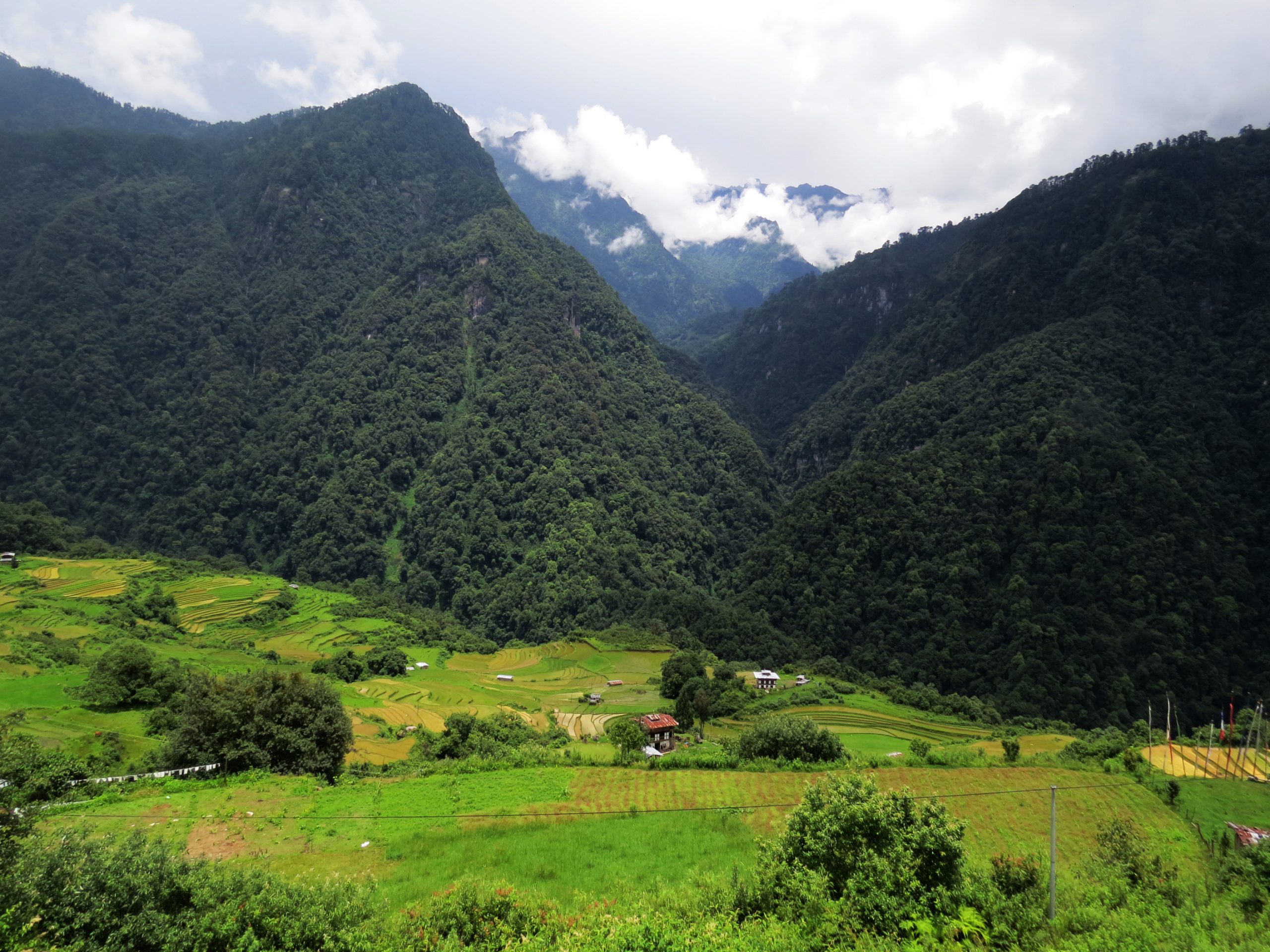
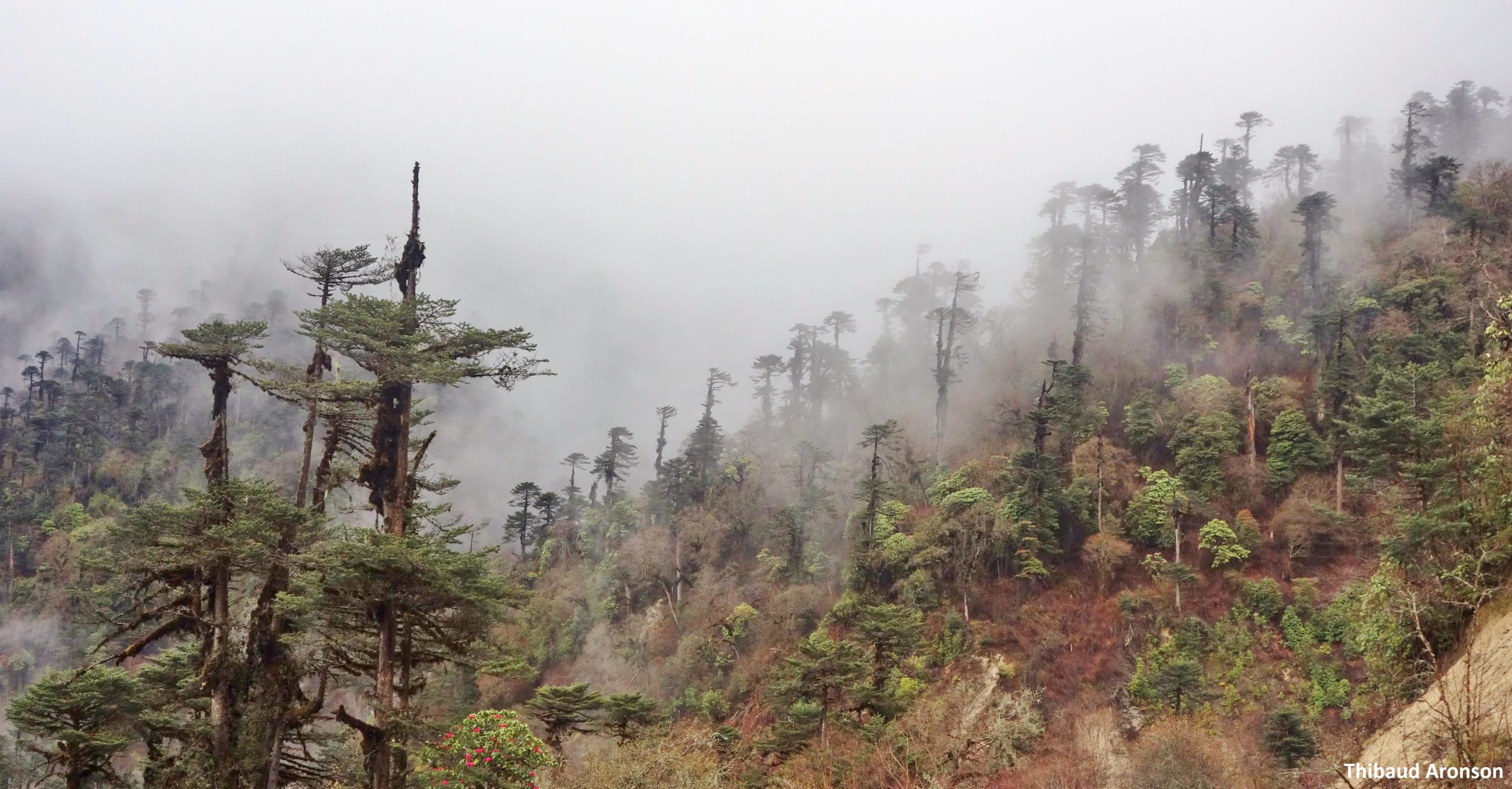
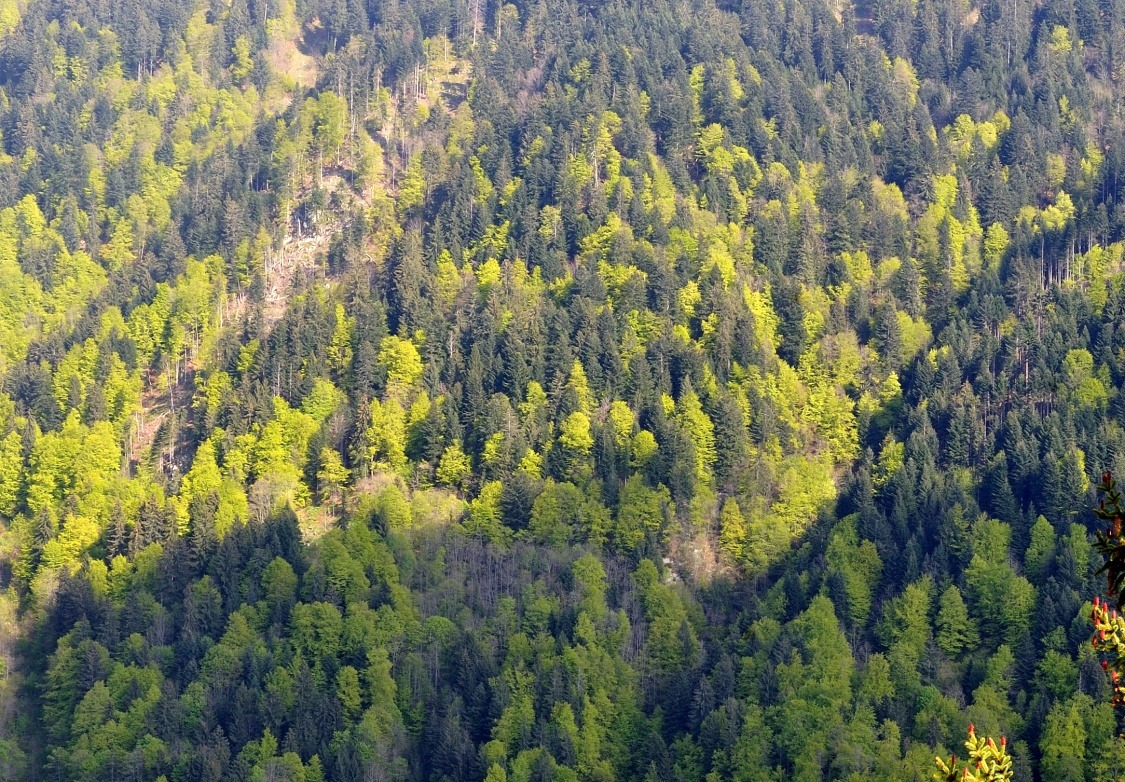
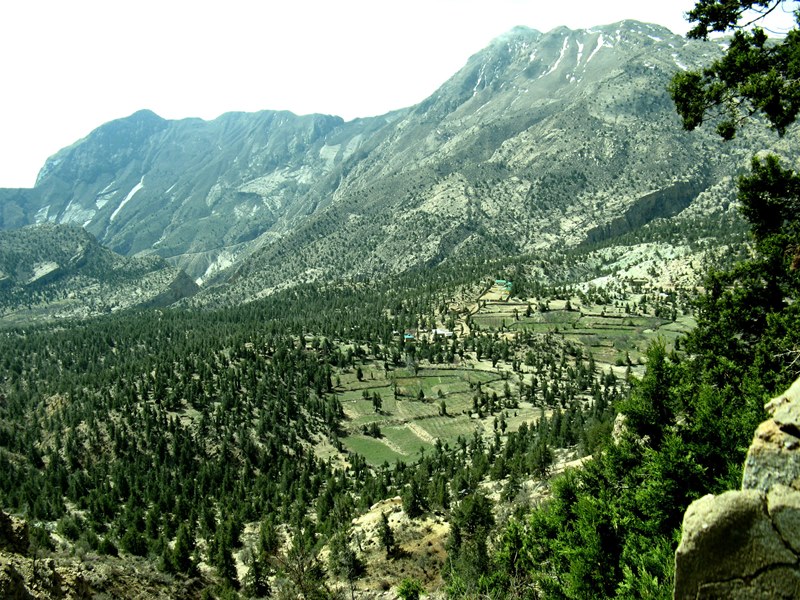
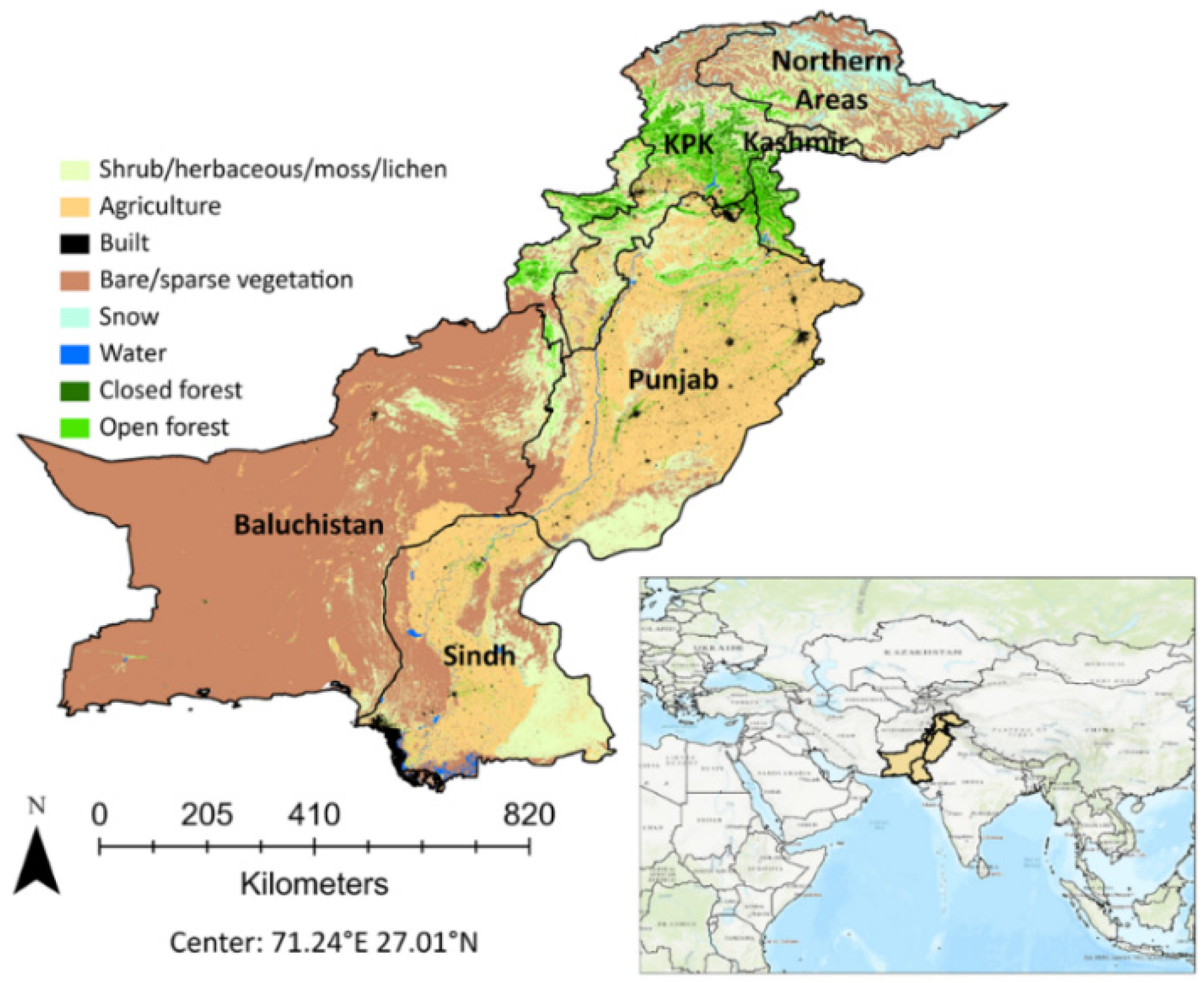
Pakistan, with its majestic snow-capped peaks, sprawling deserts, and verdant forests, boasts a landscape teeming with diversity and natural beauty. Globaleak.com takes a look at the various types of forests in Pakistan, their unique features.
Discovering the Diversity:
Pakistan’s forest landscape is as varied as it is vast. From the tranquil littoral and swamp forests gracing the shores of the Arabian Sea to the rugged charm of alpine forests adorning the lofty Himalayan peaks, each forest type beckons with its unique charm and ecological wonders.
List of Different Types of Forests in Pakistan
Prepare for an in-depth exploration as we uncover the diverse tapestry of Pakistan’s forests. Our journey will lead us through eight distinct forest types: littoral and swamp forests, tropical dry deciduous forests, tropical thorn forests, subtropical forests, subtropical pine forests, Himalayan moist temperate forests, Himalayan dry temperate forests, and alpine forests. Each ecosystem offers a unique perspective on Pakistan’s rich natural heritage, promising a deeper understanding of the country’s ecological diversity.
Let’s delve into the heart of Pakistan’s forests, where nature’s marvels await at every turn:
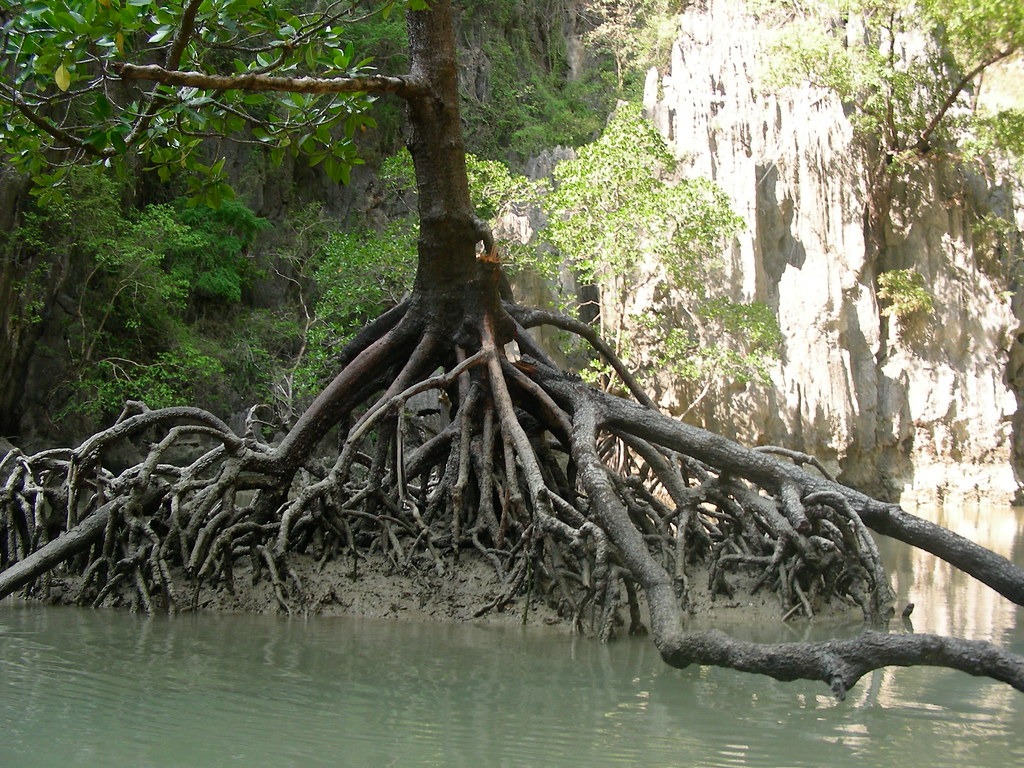
1. Littoral and Swamp Forests:
Nestled along the Arabian Sea coastline, these sprawling mangrove forests harbor exotic species like the Avicenna marina and Rhizophora, creating a haven of biodiversity across approximately 207,000 hectares of swamplands. These forests play vital roles in coastal protection, wildlife habitat, and carbon sequestration. They support diverse marine life, serve as fish nurseries, and aid in mitigating climate change. However, they face threats from habitat destruction and pollution. Conservation efforts, including protected area designation and sustainable management, are crucial to preserve the ecological integrity and biodiversity of these valuable coastal ecosystems.
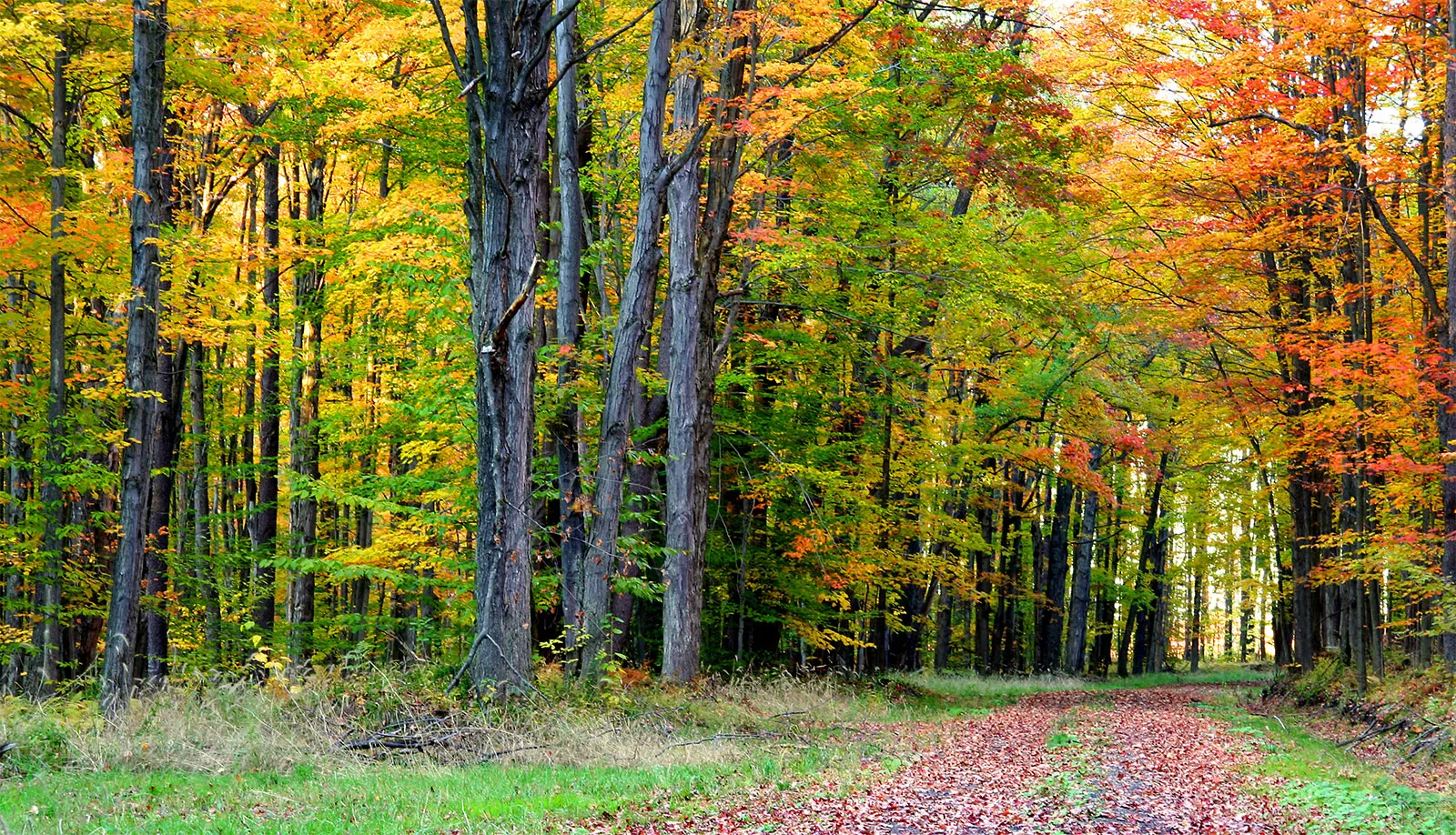
2. Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests:
With their deciduous trees shedding foliage annually, these forests come alive during the monsoon season, boasting a rich floral tapestry including Lannea, Bombax ceiba, and Acacia, among others. The Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests are predominantly found in the southern and central regions of the Pakistan, particularly in Sindh and Punjab provinces. These forests are characterized by their deciduous trees, which shed their leaves during the dry season to conserve water. Common tree species include Acacia, Dalbergia, and Tamarind. These forests endure hot temperatures and low rainfall, typical of arid and semi-arid climates. Despite the challenging conditions, they support a variety of wildlife, including deer, wild boar, and numerous bird species. However, they face threats from deforestation, overgrazing, and habitat degradation due to human activities. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the biodiversity and ecological integrity of these valuable forest ecosystems.
3. Tropical Thorn Forests:
The Tropical Thorn Forests of Pakistan, also known as the Tropical Dry Forests, are found in the southeastern regions of the country, primarily in Sindh and Balochistan provinces. Characterized by their sparse vegetation and thorny shrubs, these forests endure hot temperatures and low rainfall, typical of arid and semi-arid climates. Acacia, Prosopis, and Capparis are among the dominant plant species, adapted to survive in harsh conditions with minimal water availability. These forests provide habitat for a variety of wildlife, including desert foxes, gazelles, and numerous bird species. However, they face threats from overgrazing, deforestation, and habitat degradation due to human activities. Conservation efforts are essential to protect the biodiversity and ecological balance of these valuable ecosystems.
4. Subtropical Broadleaf Evergreen Forests:
The Subtropical Broadleaf Evergreen Forests of Pakistan thrive in the lower altitude regions, particularly in the northern and northwestern parts of the country. These forests are characterized by their lush greenery and diverse mix of broadleaf tree species that remain green throughout the year. Common species include oak, maple, chestnut, and various types of laurels. They flourish in areas with warm temperatures and abundant rainfall, creating a rich and biodiverse ecosystem. These forests provide habitat for numerous wildlife species, including leopards, monkeys, and a variety of bird species. However, they face threats from deforestation, habitat fragmentation, and climate change. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the biodiversity and ecological integrity of these valuable forest ecosystems.
5. Subtropical Pine Forests:
The Subtropical Pine Forests of Pakistan thrive in the lower altitude regions, particularly in the northwestern parts of the country. These forests are characterized by their unique blend of pine species, including the chir pine (Pinus roxburghii), which dominates the landscape. Found in areas with relatively warm temperatures and moderate rainfall, these forests play a crucial role in stabilizing soils, regulating water flow, and providing habitat for diverse wildlife such as deer, wild boar, and various bird species. However, they face threats from deforestation, illegal logging, and habitat degradation due to human activities. Conservation efforts are essential to preserve the biodiversity and ecological balance of these valuable forest ecosystems.
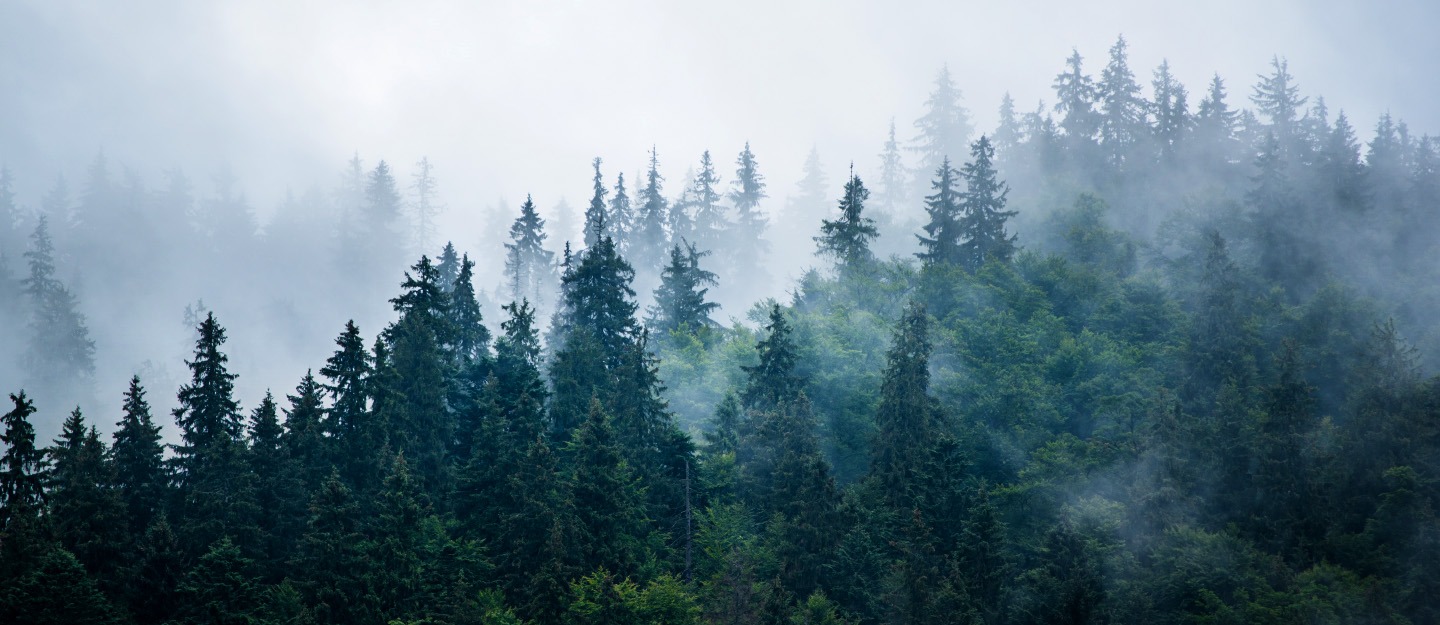
6. Himalayan Moist Temperate Forests:
The Himalayan Moist Temperate Forests of Pakistan thrive in the lower to mid-altitude regions of the Himalayas and adjacent ranges. Known for their lush greenery and moderate climates, these forests experience ample rainfall and cooler temperatures compared to their dry temperate counterparts. They are characterized by a diverse mix of tree species including oak, maple, rhododendron, and deodar cedar. These forests provide habitat for a wide range of wildlife, including Himalayan black bear, leopard, and various bird species. However, they face threats from deforestation, habitat fragmentation, and climate change. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the biodiversity and ecological integrity of these vital ecosystems.
7. Himalayan Dry Temperate Forests:
The Himalayan Dry Temperate Forests of Pakistan are an integral part of the country’s diverse ecosystem, found in the foothills of the Himalayas and Karakoram ranges. Characterized by sparse vegetation and a semi-arid climate, these forests endure long, dry summers and harsh winters. Dominated by species such as blue pine, chir pine, and oak, they support a range of wildlife including Himalayan brown bear, markhor, and various bird species. Threatened by deforestation and habitat degradation, conservation efforts are vital to safeguard these forests and the biodiversity they harbor, ensuring their resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
8. Alpine Forests:
The Alpine Forests of Pakistan, nestled in the towering peaks of the Himalayas, Karakoram, and Hindu Kush ranges, are characterized by rugged terrain, harsh climates, and unique biodiversity. Found at elevations above the treeline, typically above 3,000 meters, these forests showcase resilient species such as juniper, pine, and birch, adapted to extreme cold and thin soils. Despite the challenges, they support a variety of wildlife including snow leopards, ibex, and various bird species. Threatened by climate change and human activities, conservation efforts are crucial to protect these fragile ecosystems, ensuring their survival for future generations.Top of Form
Unveiling Natural Treasures:
As we traverse the forested landscapes of Pakistan, certain gems stand out amidst the verdant tapestry:
· Ziarat Juniper Forest:
Nestled in the picturesque city of Ziarat, this sprawling expanse of juniper trees is not only a sight to behold but also a vital ecological lifeline, preserving soil and water resources for generations to come. Covering an area of approximately 110,000 hectares, it is the second-largest Juniper forest in the world and is renowned for its natural beauty and biodiversity. The Juniper trees found in this forest are some of the oldest living trees on earth, with some estimated to be over 5000 years old. These resilient trees have adapted to the harsh mountainous terrain and arid climate of the region, making them a symbol of endurance and strength. This Forest serves as a crucial habitat for various wildlife species, including Himalayan ibex, foxes, and a variety of bird species.
· Changa Manga Forest:
Known for its vast expanse and unique canal system, the Changa Manga Forest is a testament to Pakistan’s commitment to conservation and sustainable forestry practices, offering sanctuary to diverse flora and fauna, spanning over 12,400 acres. Established in 1866 during British rule, it is one of the oldest and largest man-made forests in the world. The name “Changa Manga” is derived from the names of two nearby villages. It serves as an important habitat for indigenous species and plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance in the region.
The Forestry Sector in Pakistan
In the heart of Pakistan’s natural bounty lies the forestry sector, a vital engine driving economic growth, environmental sustainability, and cultural heritage preservation. Let’s delve into the diverse array of contributions made by this sector, illuminating its pivotal role in shaping the nation’s landscape and livelihoods.
I. A Cornucopia of Resources:
The forestry sector stands as a veritable treasure trove, yielding a rich harvest of lumber, paper, fuelwood, latex, and medicinal plants. Beyond mere sustenance, these resources form the backbone of numerous industries, fueling economic development and innovation across the nation.
II. Nurturing Nature’s Bounty:
At the intersection of ecology and economy, Pakistan’s forests serve as vital ecosystems, providing not only food but also shelter and sustenance to a myriad of plant and animal species. Moreover, they serve as invaluable hubs for ecotourism and wildlife conservation, inviting visitors to marvel at nature’s splendor while fostering a deeper connection to the natural world.
III. A Testament to Diversity:
Covering 4.91% of Pakistan’s land, forests weave a tapestry of biodiversity and ecological resilience, each region contributing its own unique charm and character to the nation’s natural heritage. Notably, the Shangla district emerges as a beacon of forested splendor, with over 80% of its land adorned in lush greenery—a testament to the district’s commitment to conservation and sustainability.
IV. Preserving the Past, Securing the Future:
As custodians of this natural legacy, it is incumbent upon us to safeguard and steward Pakistan’s forests for generations to come. Through responsible management practices, community engagement, and policy innovation, we can ensure that these invaluable resources continue to enrich our lives, sustain our ecosystems, and inspire wonder for centuries to come.
Importance of Forests in Pakistan
Forests in Pakistan are not just patches of greenery; they are lifelines, intricately woven into the fabric of our existence. From regulating the water cycle and mitigating soil erosion to moderating the climate and preserving biodiversity, these forests play a multifaceted role in sustaining life and safeguarding our planet’s delicate balance.
i. Biodiversity: Guardians of Ecological Diversity
At the heart of Pakistan’s forests lies a treasure trove of biodiversity, harboring a kaleidoscope of plant and animal species found nowhere else on Earth. By preserving these ecosystems, we not only protect rare and endangered species but also ensure the resilience and adaptability of our natural world in the face of environmental challenges.
ii. Carbon Reduction: Nature’s Carbon Sinks
In an era of climate change and carbon emissions, Pakistan’s forests emerge as invaluable allies in the fight against global warming. As carbon sinks, these wooded realms absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating greenhouse gas levels and curbing the adverse effects of climate change on our planet’s delicate ecosystems.
iii. Water Regulation: Guardians of the Watershed
From the mighty rivers to the humble streams, Pakistan’s forests stand as guardians of the watershed, regulating water flow and safeguarding against floods and droughts. By preserving these vital ecosystems, we ensure a steady supply of water for human consumption, agriculture, and wildlife, thus nurturing life across the land.
iv. Climate Regulation: Nature’s Climate Engineers
In the ever-changing tapestry of climate patterns, Pakistan’s forests emerge as nature’s climate engineers, providing shade, releasing oxygen, and cooling the air. By mitigating the effects of urban heat islands and fostering microclimates of biodiversity, these forests forge a harmonious balance between man and nature.
v. Ecotourism: Gateway to Sustainable Development
Beyond their ecological significance, Pakistan’s forests offer a gateway to sustainable development through ecotourism. By attracting visitors from around the globe, these natural wonders not only contribute to the local economy but also foster greater awareness and support for conservation efforts, ensuring their preservation for generations to come.
Championing Conservation:
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, Pakistan’s forests play a pivotal role in sustaining life, mitigating climate change, and fostering biodiversity. As stewards of this natural heritage, it is our collective responsibility to safeguard these forests for future generations.
Conclusion:
In traversing the diverse realms of Pakistan’s forests, we uncover not just ecological wonders but also timeless treasures that enrich our lives and sustain our planet. Let us pledge to preserve and protect these invaluable ecosystems, ensuring a greener, more sustainable future for all.
Join us in celebrating the magnificence of Pakistan’s forests—a true testament to nature’s boundless beauty and resilience.
Read Also:
- What Tourists Attractions Are Famous In Karachi?
- What Do You Know About Public Transport In Pakistan?
- What Tourists Destinations Are Most Famous In Pakistan?
📍 SEO & Content Strategist | Expert in Current Affairs, History, Geography & Education Blogs | Digital Marketing Specialist
Muhammad Talha Mehmood is a seasoned digital marketing specialist, SEO expert, and content strategist with over six years of experience in creating high-impact, research-driven content. As the driving force behind Globaleak.com, he delivers in-depth articles on current affairs, history, geography, and education, helping readers stay informed with accurate, well-researched insights.
🔹 Expertise & Achievements:
✔ SEO & Content Strategy: Specializes in creating authoritative, high-ranking content that aligns with Google’s EEAT guidelines.
✔ Research & Analysis: Covers historical events, geopolitical trends, and educational topics with in-depth research and expert insights.
✔ Proven Track Record: Has successfully worked with global clients, delivering content that enhances brand trust, audience engagement, and search rankings.
✔ Academic Excellence: Holds an MBA in Marketing from IBA, University of the Punjab, and a B.Com (Hons) from Hailey College of Commerce.
✔ Industry Experience: Started his career with Packages Limited, trained under PITB’s E-Rozgar Program, and later became a Team Leader & Trainer at Emenac Group of Companies.
🚀 Passionate about creating impactful content, Muhammad Talha ensures every article is insightful, engaging, and value-driven.
📧 Email: talhamehmood34@gmail.com
🔗 LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/talhamehmood-34